A digital method for structure matching between large spacecraft and external heat flux simulation device
-
摘要: 在航天器真空热试验中,常选用红外加热笼作为外热流模拟装置。为提高外热流模拟的准确性,红外加热笼需要对航天器进行全表面覆形。文章针对如何确认外热流模拟装置与航天器的结构匹配性这个难题,依托三维扫描技术,建立了一套数字化结构匹配方法,解决了多站测量拼接误差累积、三维扫描仪参数优化选择2个技术难点,使三维扫描和逆向建模过程引入的几何误差不超过10 mm。该数字化结构匹配方法的实际应用结果表明,外热流模拟装置与航天器的配装成功率达到100%,实际安装状态与仿真结果吻合度较好。Abstract: The infrared heating cage is often used as the external heat flux simulation device in the thermal vacuum test (TBT& TVT) for spacecraft. To conduct an accurate simulation of the heat flux, the infrared heating tape array is supposed to cover the whole surface of the spacecraft. To solve the difficulties in confirming the structural matching degree between the spacecraft and the infrared heating cage in the test, a set of digital structure matching methods is adopted based on the 3D scanning technology. The set of methods is successful in reducing the accumulated error during the data splicing and in optimizing the parameters of the 3D scanner. The total geometric error of the 3D scanning and the reverse modeling is not more than 10 mm. By using this set of methods, the structural matching is completely achieved between the heat flux simulation device and the spacecraft. In the meantime, the actual installation state is in good agreement with the simulation results.
-
0. 引言
在真空热试验中,常选用红外加热笼作为外热流模拟装置。为提高外热流模拟的准确性,红外加热笼需要对航天器进行全表面覆形,与航天器表面距离一般控制在300 mm左右。大型航天器包含多个结构舱段,外形尺寸大、表面结构状态复杂,因其表面有大量外露设备超出了红外加热笼与航天器表面的间距控制范围而需对红外加热笼开孔进行结构避让。为了减小红外加热笼开孔对外热流模拟准确性的影响,这些开孔应尽量小,开孔边界与凸出设备的几何容差应控制在50 mm左右。红外加热笼为分块框架型结构,采用二维模式设计与加工,使用不锈钢管、角形钢等标准材料焊接而成,其加工尺寸误差一般在20 mm左右。
红外加热笼与航天器的结构匹配主要存在如下问题:1)大尺寸框架型结构焊接的加工尺寸误差大,约占设计容差的40%;2)传统尺寸测量方法对圆锥、圆台、球等曲面空间位置的测量误差大,导致红外加热笼加工尺寸验证困难;3)采用实物试装配的方法提前对红外加热笼与航天器进行结构匹配验证的代价太大,需要占用1星期以上的主线研制时间,并耗用大量的人力资源;4)航天器表面部分软性结构的实施状态与航天器结构设计存在差异。
三维扫描技术主要用于对物体空间外形、结构及色彩进行扫描,以获得物体表面的空间坐标。该技术能实现非接触测量,具有速度快、精度高的优点[1],且其测量结果能直接与多种软件接口。因此,三维扫描技术在制造业[2]、建筑业[3]、文物考古[4]及生物医学[5]等方面得到了广泛应用。在汽车和航空制造行业中,三维扫描技术已经基本替代了传统的三坐标测量检测方式用于涡轮增压叶片和航空发动机叶片的检测;大型汽车工厂已经完成主要部件三维扫描流水线的布设,通过三维扫描仪和工业机器人的结合,使用计算机软件自动控制整个检测和分析过程,极大提高了产品检测的准确度和效率。
针对外热流模拟装置与大型航天器结构匹配的问题,本文提出基于三维扫描技术的数字化结构匹配方法:首先利用三维扫描技术获取外热流模拟装置或航天器实物的结构表面空间坐标(点云数据),然后构建外热流模拟装置或航天器的实物三维模型,最后利用三维软件对所构建的模型进行结构匹配验证。
1. 数字化结构匹配方法及流程
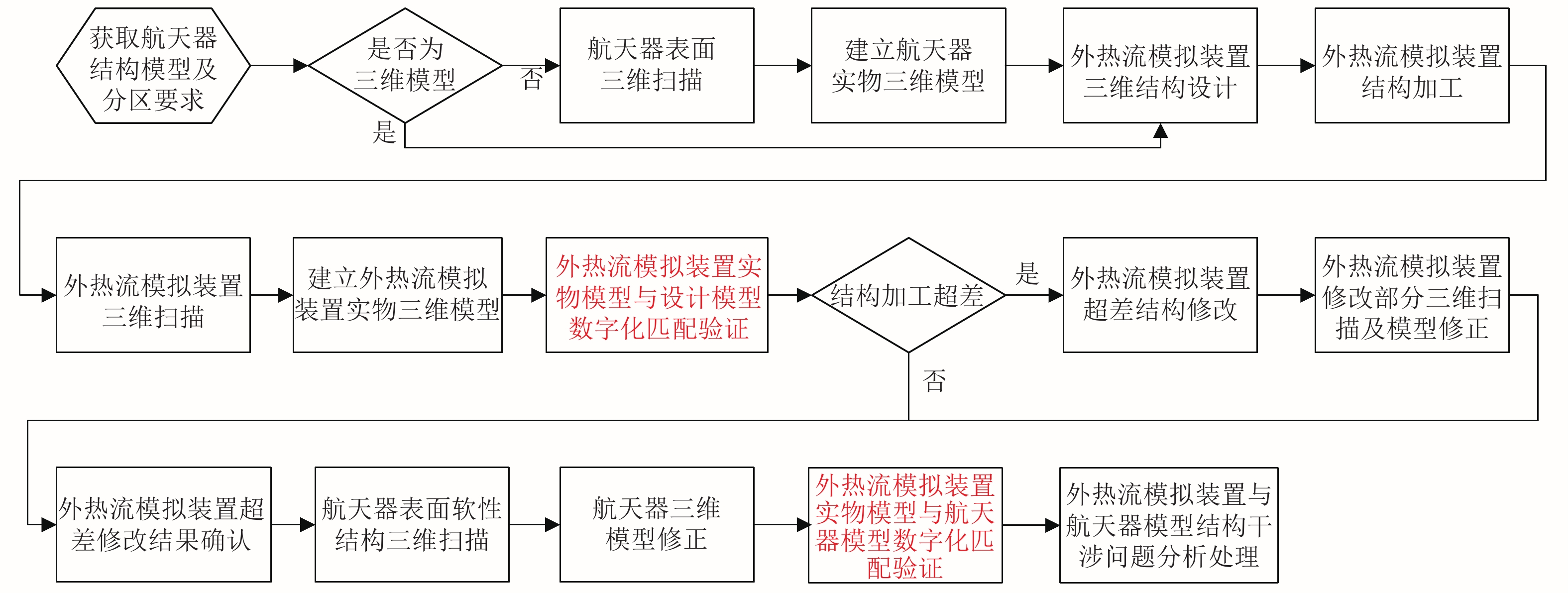
外热流模拟装置结构设计主要以航天器结构模型及分区要求作为设计输入,其中分区要求规定了航天器表面加热区域的划分及外热流模拟装置与航天器表面的距离。部分航天器结构模型仍为二维模型,既无法进行结构匹配验证,也给外热流模拟装置的结构设计带来不便,因此需对这类航天器的表面结构进行三维扫描,建立与实物对应的三维结构模型(简称实物三维模型),以作为外热流模拟装置结构设计的依据。
外热流模拟装置结构设计、加工完成后,需要对其实物进行三维扫描,建立实物三维模型,将实物三维模型与三维设计模型进行数字化匹配验证,以确认外热流模拟装置的结构加工误差是否在要求范围内;如存在超差情况,则须对超差部分的外热流模拟装置进行结构修改;修改完成后,对修改的部分进行三维扫描,并利用扫描结果进行外热流模拟装置实物三维模型的修正,再次进行三维实物模型与设计模型的比对,以确认尺寸超差的修改结果是否满足要求。
在航天器进行热试验前,其结构表面要铺设大量电缆和包覆软性材料,这些软性结构无法在航天器设计模型中准确给出,因而造成航天器实物与其三维模型之间存在差异。因此,在航天器表面电缆和软性结构实施完成后,须对航天器表面的软性结构进行扫描,建立其三维包络模型,并据此对航天器的三维模型进行修正,以提高模型与实物的贴合度。利用修正后的航天器模型与红外加热笼模型进行数字化结构匹配,以确认两者是否存在结构干涉(隐患);如发现干涉(隐患),须进行原因分析并采取措施予以消除。
整个数字化结构匹配方法的流程如图1所示。
2. 数字化结构匹配方法中的关键技术
2.1 三维扫描及逆向建模的几何精度要求
外热流模拟装置在设计时预留的几何容差为50 mm,从大量的实际经验来看,红外加热笼与航天器的安全距离至少应控制在30 mm左右,因此留给数字化结构匹配的几何容差为20 mm;数字化结构匹配中航天器和红外加热笼均需要进行三维扫描和逆向建模,因此单次过程的几何容差最大为10 mm。
三维扫描和逆向建模过程引入的几何误差主要来自:1)三维扫描仪的测量误差;2)多站测量点云数据的拼接误差;3)逆向建模时的数据处理误差。以上三者的累积不可超过10 mm,推荐的误差分配为:扫描误差≤4 mm,拼接误差≤3 mm,逆向建模数据处理误差≤3 mm。
2.2 三维扫描的布站原则
在进行航天器或外热流模拟装置三维扫描前,需要根据现场环境规划扫描站点和标靶点的布置,以保证尺寸数据扫描的完整性和拼接精度,一般遵循如下原则:
1)使扫描设站以及标靶点(参考球或纸质标靶)分布尽量均匀,扫描站点之间要有30%的重复区域;
2)对于重点扫描区域,应多角度多方位架设站点以保证扫描数据完整性在90%以上;
3)参考球应布设在两扫描测站中间,两站之间至少有3个可视的参考球,参考球之间应有一定的高度差,以保证两扫描测站之间的数据能正常拼接;
4)纸质标靶的布设最好与扫描仪视角方向成垂直角度,距离尽量控制在10 m以内。
2.3 多站测量拼接误差累积问题的处理
对于现场环境复杂,航天器或外热流模拟装置周围存在工装阻隔扫描仪可视区域的情况(如航天器在大型操作平台内部进行总装),需要大量增加扫描站数以保证数据的完整性;但是随着扫描站数的增加,通过站间标靶点进行数据拼接的处理方法会导致拼接误差的累积。这种情况下,采用全站仪对各扫描站点数据进行控制,可以大大降低因扫描站数增多带来的拼接误差累积。
使用全站仪进行扫描站点数据控制的方法为:1)布置全站仪,建立基准坐标系;2)按照布站规划进行扫描,每站至少保证3个可视的参考球;3)使用全站仪测量每个参考球的空间坐标;4)在SCENE软件中导入坐标文件,手动指定参考球空间坐标,强制进行对应扫描数据的拼接。在这种方法中,推荐使用ATS大参考球配合棱镜的方式进行空间位置的测量,最后扫描数据的拼接误差即为全站仪的测量误差,一般可以控制在2 mm左右。
以某次测试为例,航天器外包络高度方向尺寸约10 m,直径约3 m,位于5层操作平台中,需要分层进行扫描,每层扫描4站。三维激光扫描仪采用FARO Focus X330,全站仪使用徕卡TCRP1201,总扫描站数为23站。采用站站间参考球进行扫描点云数据的拼接,SCENE软件统计的拼接误差平均值为8.7 mm;采用全站仪进行扫描站点数据控制拼接,SCENE软件统计的拼接误差平均值为1.4 mm。选取航天器底部与顶部2个端面作为标准比对平面,两平面设计高度差为8 180.0 mm,分别对用以上2种方法拼接出的数据进行平面拟合,以轴心作为中心,在圆周上按120°均布的方式提取2个平面的高度差,站站拼接方式和全站仪控制拼接方式得到的高度差平均值分别为8 168.1和8 183.1 mm,可见全站仪控制拼接方式的误差要明显小于站站拼接方式的误差。详细数据如表1所示。
表 1 站站拼接与全站仪控制拼接误差对比Table 1. Comparison of deviations between two different methodsmm 拼接方式 设计标准值 测试点1 测试点2 测试点3 平均值 平均误差 最大误差 站站拼接 8 180.0 8 169.4 8 166.8 8 168.2 8 168.1 11.9 13.2 全站仪控制拼接 8 183.9 8 182.8 8 182.6 8 183.1 3.1 3.9 2.4 三维扫描仪参数的选择
三维扫描仪的扫描参数决定了扫描时长、测试精度以及数据量的大小。在满足测试精度的基础上,选择合适的扫描参数,可以节省扫描时长,降低扫描数据量,以便后期计算机能更快地处理数据。
扫描参数包括扫描质量和扫描步长。扫描质量是指扫描时对单个测点进行激光测距的测量次数,通过多次测量可提高测距精度。扫描步长是指扫描仪扫描相邻测量点时扫描头的旋转角度,分为垂直步长和水平步长,其决定了被测表面的几何采样分辨率。扫描参数的选择一方面要考虑扫描误差的要求,另一方面要考虑扫描点云处理软件对参考球识别的要求,一般软件推荐参考球上的扫描点数要>100。
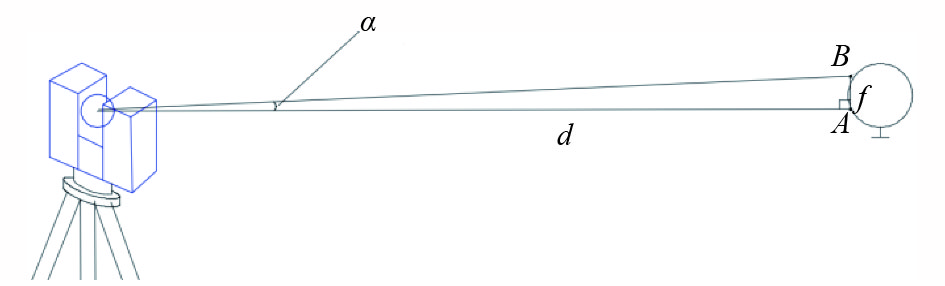
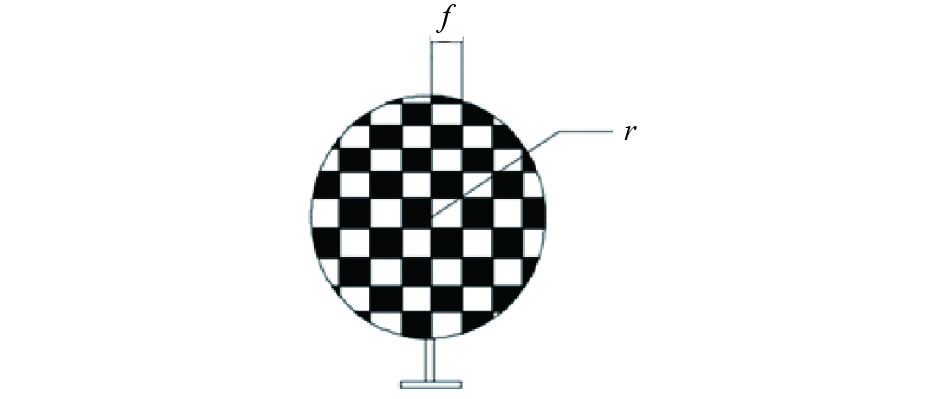
如图2所示,设扫描仪的水平步长为角α;A、B为扫描到被测物体表面的相邻两点;d为扫描仪到A点的距离;f为A、B两点的间距。f相对于d很小,故可以认为d与f之间为直角,则tan α=f/d,f=dtan α。f应不大于扫描误差(4 mm),当d较小时,可以增加扫描步长,以提高扫描速度,节省扫描和后期数据处理的时间。另外,参考球半径r一般在100 mm左右,在其摆放距离与被测物尺寸相当的情况下,要保证扫描误差≤4 mm,参考球上的扫描点数应>100,以满足软件识别的要求;在其摆放距离为被测物尺寸2倍以上的情况下,需要考虑参考球上扫描点的数量来确定扫描步长,如图3所示。
2.5 三维扫描点云数据的处理
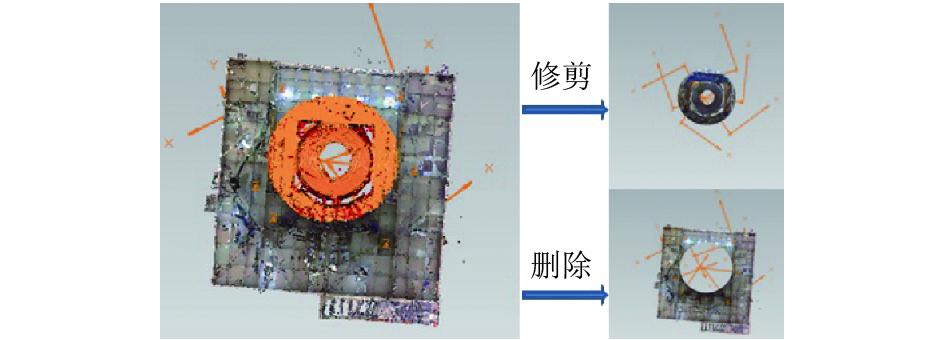
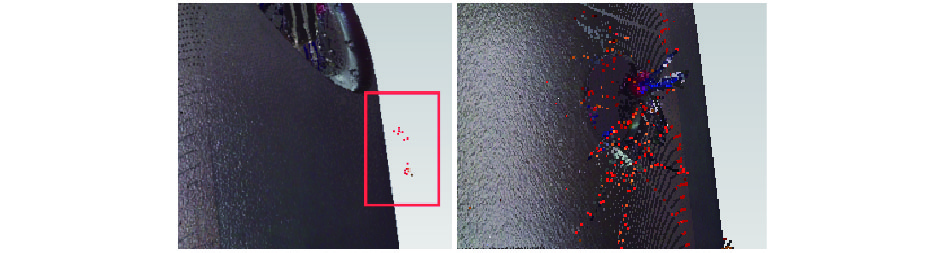
三维扫描仪在工作过程中,每站扫描都会采集到测距范围内的所有可视点;另外,由于被测物表面材质反射率的影响,会产生测试噪声点,这些都包含在原始点云数据中。原始点云数据中所包含的大量无关数据和噪声数据会给后期逆向建模带来干扰,因此点云数据处理的第1步就是剔除无关点和噪声点。SCENE软件可以按一定距离过滤掉部分无关的点,更多的点处理过程则需要使用专业的点云处理软件(如GEOMAGIC软件),如非连接点和体外孤点的剔除,处理示例见图4、图5所示。
数据处理的第2步是进行所有扫描数据的采样、抽稀和简化,通过数据点云软件统一采样功能对点云进行数量优化,统一点云数据的点间距、减少点数量。对于平整面可以设置点间距为10 mm进行优化,对存在拐点的复杂区域可设置点间距为2~3 mm保留细节,再将局部数据替换到整体数据中。这样既减少了形状简单的平整面的数据量,又保证了局部位置的精细程度。
2.6 逆向建模
对于几何尺寸大的航天器或外热流模拟装置,点云数据处理完成后,可利用点云数据处理软件生成STL标准的三角网格数据,以便Pro/E三维建模软件能顺利打开,一般图形工作站中使用单个STL格式的三角网数据不能超过3 000 000面数。根据航天器或外热流模拟装置的实际结构形式,依托三角网数据构建其三维结构模型,构建完成后利用软件功能统计三维结构模型与三角网数据的几何尺寸误差,并将误差控制在3 mm内,以确保整个处理流程的精度满足要求。
3. 应用情况
自2015年以来,该数字化结构匹配方法已应用于多个航天器真空热试验,经过数字化结构匹配后,外热流模拟装置与航天器的配装成功率达到100%,实际安装状态与仿真结果吻合度较好。该数字化结构匹配方法的部分应用场景如图6、图7所示。
4. 结束语
数字化结构匹配方法通过对三维扫描技术及数字建模技术的整合,解决了外热流模拟装置加工尺寸验证和与航天器结构匹配困难的问题,具有不占用航天器主线研制时间、不存在操作安全风险等优点,是实现尺寸不大于20 m外热流模拟装置与航天器结构匹配的理想解决方案。
该方案还能用于其他复杂地面工装以及航天器之间的结构干涉验证,具有很好的通用性。
-
表 1 站站拼接与全站仪控制拼接误差对比
Table 1 Comparison of deviations between two different methods
mm 拼接方式 设计标准值 测试点1 测试点2 测试点3 平均值 平均误差 最大误差 站站拼接 8 180.0 8 169.4 8 166.8 8 168.2 8 168.1 11.9 13.2 全站仪控制拼接 8 183.9 8 182.8 8 182.6 8 183.1 3.1 3.9 -
[1] 杨俊志, 尹建忠, 吴星亮. 地面激光扫描仪的测量原理及其鉴定[M]. 北京: 测绘出版社, 2012: 1-2 [2] 陶京新, 刘大亮, 胡文刚, 等. 机器人激光三维扫描技术在壳体自动测量中的应用[J]. 制造业自动化, 2017, 39(1): 76-78 TAO J X, LIU D L, HU W G, et al. Application of robot laser 3D scanning technology in automatic measurement of shell[J]. Manufacturing Automation, 2017, 39(1): 76-78
[3] 冯腾, 吴长悦. 三维激光扫描技术在土方测量中的应用[J]. 山西建筑, 2015, 41(22): 203-204 FENG T, WU C Y. On application of three-dimension laser scanning technique in earthwork measurement[J]. Shanxi Architecture, 2015, 41(22): 203-204
[4] 周曦冰, 甘淑, 刘广辉, 等. 三维扫描古栈道本体图绘制[J]. 测绘科学, 2017, 42(3): 53-56 ZHOU X B, GAN S, LIU G H, et al. Drawing tests and analysis of ancient plank road ontology graph using 3D laser scanning technology[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2017, 42(3): 53-56
[5] 柳光茂, 周建业, 胡盛寿, 等. 基于激光三维扫描技术的微型轴流血泵叶轮加工精度检测[J]. 北京生物医学工程, 2012, 31(4): 338-341 LIU G M, ZHOU J Y, HU S S, et al. Machining precision detection for impeller of micro-axial blood pump based on 3D laser scanning technology[J]. Beijing Biomedical Engineering, 2012, 31(4): 338-341
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 黄春玮,张旭升,郭亮. 基于微型空间相机的红外加热笼仿真与设计. 红外技术. 2024(02): 138-143 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王国防,刘家林,孙成恺,刘海静,张静,董德胜. 一种高精度外热流模拟控制系统设计与研究. 真空. 2024(04): 65-70 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 付春雨,范超. 基于组合热流模拟策略的遥感卫星热平衡试验设计与验证. 航天器环境工程. 2024(04): 497-502 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 李涛,敬铮,王为,何向君,罗皓. 载人航天器数字化研制方法与应用. 载人航天. 2023(04): 513-520 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 崔云先,黄金鹏,曹凯迪,王浩宇,殷俊伟. 新型高温薄膜热流传感器的研制. 仪器仪表学报. 2021(03): 78-87 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 于洋,杨国栋,田宇沃,张航,张庆新. 谱共轭梯度算法反演航天器在轨瞬态外热流. 沈阳航空航天大学学报. 2020(03): 62-67 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: